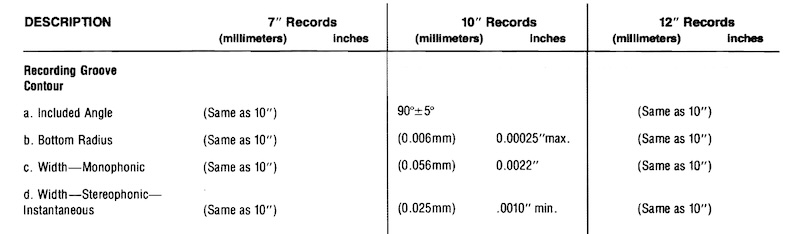
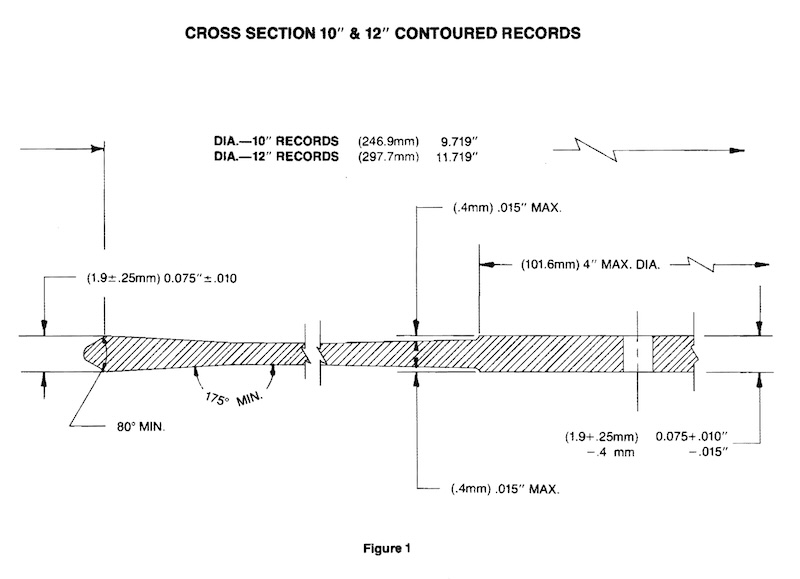
How Records Were/Are Manufactured (4)
第1回、第2回、第3回 に続き、戦後のレコード製造工程や原材料の歴史、特に 射出成形 と スチレン盤 について改めて調べてみた、そんな記録です。
Following on from the first, second and third parts, this is a record of a renewed look into the history of postwar record manufacturing processes and raw materials, particularly injection molding and styrene records.
4回目となる今回は、1954年当時の射出成形 vs 圧縮成形の様子を解説した記事をかわきりに、1950年代末には結局LP盤のほとんどが圧縮成形プレスで製造されていたこと、逆に射出成形スチレン盤は7インチシングル盤として米国で広く普及したこと、その他1960年代のさまざまなエピソードをみていきます。
This time, the fourth part, begins with an article from 1954 explaining the state of injection molding vs compression molding. We will then go on to look at how by the end of the 1950s, most LPs were produced using compression molding presses, how injection-molded styrene records became widely used in the United States as 7-inch singles, and other various episodes from the 1960s.
21世紀の現在、新しい文脈から射出成形12インチLP盤が再登場していますが、当時の技術レベル(や当時のレーベルの経営的思惑)からは、射出成形LP盤は主流になれなかったのだろう、そんな風に思わされました。
Now in the 21st century, injection-molded 12-inch LPs are making a comeback in a new context, but it seems to me that given the level of technology at the time (and the business intentions of the labels at the time), injection-molded LPs probably could never became mainstream.
Continue reading